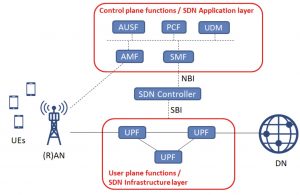
AAS (Active Antenna System), an active antenna system, can be seen as a combination of RRU and antenna, which integrates an active radio frequency transceiver unit and a passive antenna array.
In the past, the RRU and the antenna were separated, and the two were connected through a radio frequency feeder. After integrating the RF transceiver unit and antenna array, AAS can support Massive MIMO technology, which can reduce RF feeder loss, increase network coverage and capacity, and reduce sky space and maintenance workload.
AF (Application Function), application function. AF is similar to an application server, which interacts with other 5G core network control plane NFs and provides business services. AF can exist for different application services, and can be owned by an operator or a trusted third party.
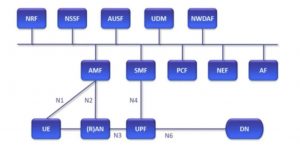
AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function), access and mobility management function. AMF is responsible for functions such as UE identity verification, authentication, registration, mobility management, and connection management. Compared with 4G EPC, the function of AMF is similar to that of MME.
AUSF (Authentication server function), the authentication server function, is responsible for authentication and authentication.
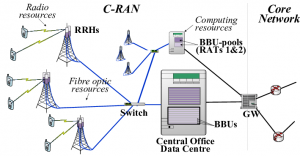
Backhaul, backhaul, refers to the transmission network that connects the radio access network (RAN) and the mobile core network. Under the distributed RAN (D-RAN) architecture, backhaul connects the base station to the core network; under the centralized RAN (C-RAN) architecture, it connects the centrally deployed cloud BBU/DU pool to the core network.
BBU (Baseband Unit) refers to the unit responsible for processing baseband signals in the base station system.
Beamforming, beam forming. Radio waves are like waves. When they collide (interfere) with each other, they become stronger or weaker, depending on how they collide. Beamforming takes advantage of this feature. It transmits the same signal through multiple antenna units, and adjusts the phase and amplitude of each antenna unit, so that radio waves are enhanced in a specific direction, and they cancel each other out and weaken in other directions. Make wireless signal propagation more concentrated like beams, which can increase coverage and reduce interference.
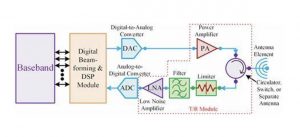
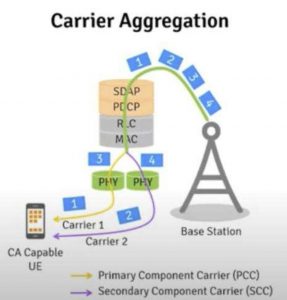
CA (Carrier Aggregation), carrier aggregation, is to aggregate two or more carriers (channels) to provide users with a higher data rate. CA is like merging two or more roads together to make the road wider.
Control Plane, the control plane, is mainly responsible for processing non-data packet forwarding, including control signaling such as mobility management, connection establishment, and quality of service (QoS).
C-RAN (Centralized/Cloud-Radio Access Network), centralized/cloud-based radio access network), C stands for Centralized, Cloud, Clean and Cooperative, and refers to the centralized and cloud-based/virtualized deployment of CU and DU , Which can improve the coordinated scheduling between cells, achieve more flexible resource scheduling and load balancing, and reduce deployment and operation and maintenance costs.
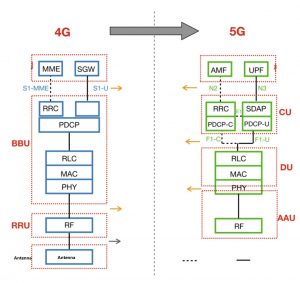
CU (Centralized Unit), the central unit. 4G base station equipment is composed of BBU (baseband unit) and RRU (remote radio unit). The RRU is usually extended to a place close to the antenna. The BBU and the RRU are connected by optical fiber, and the RRU and the antenna are connected by a feeder. The 5G base station equipment divides the BBU into CU (Central Unit) and DU (Distributed Unit), and is connected to AAU (Active Antenna Unit) through optical fiber. The CU is responsible for hosting the RRC (Radio Resource Control Layer), SDAP (Service Data Adaptation Protocol) and PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol Layer) sublayers of the 5G base station, which centrally controls one or more DU units.
CUPS (Control and User Plane Split), the separation of control plane and user plane functions, refers to the separation of the control plane functions responsible for connection management, QoS policies, user authentication and other functions from the user plane functions responsible for data traffic forwarding to simplify and unify The entire network architecture makes the core network more flexible and efficient. Under the CUPS architecture, as the number of traffic increases, user plane functions can be independently expanded without affecting the control plane, and it is also convenient for centralized management of the control plane.